
지난 27일 새벽, 대한민국 밤하늘을 가르며 쏘아 올려진 한국형 발사체 '누리호'가 네 번째 비행을 성공적으로 마쳤습니다. 이번 발사는 단순한 성공 이상의 깊은 의미를 지닙니다. 바로 체계종합기업인 한화에어로스페이스가 기체 제작을 전담하고 발사 준비 및 운용 과정에 본격적으로 참여하여, '민간 주도 우주 개발(New Space)'의 가능성을 실전에서 입증한 첫 사례이기 때문입니다.
특히 이번 성공의 이면에는 대한민국 우주항공 제조 기업들의 헌신적인 공헌이 있었습니다. 연료 탱크부터 엔진 지지 구조물, 발사체 신경망인 전기 커넥터와 단열재에 이르기까지, 수만 개의 부품이 오차 없이 결합되어야만 가능한 이 거대한 도전은 우리 제조 기업들이 보유한 세계적인 수준의 기술력과 생산 능력이 있었기에 가능했습니다.
이제 대한민국 우주 산업은 국가 주도의 R&D 단계를 넘어, 민간 기업이 주도하는 상용화 및 산업화 단계로 진입하고 있습니다. 하지만 이러한 전환기에는 ‘더 빠르고, 더 효율적이며, 더 정밀한 제조’라는 과제가 뒤따릅니다. 발사 공백을 최소화하고 기술 인력과 공급망을 유지하기 위해서는 제조 프로세스의 혁신이 필수적입니다.
이러한 과제를 해결하고 '뉴 스페이스' 시대를 앞당길 핵심 기술, 바로 산업용 3D프린팅(적층 제조)입니다. 오늘은 글로벌 우주항공 리더들이 어떻게 3D프린팅을 활용하여 R&D 속도를 혁신하고 있는지, 보잉(Boeing)과 NASA의 최신 사례를 통해 알아보겠습니다.
Boeing(보잉): 3D프린팅으로 위성 생산 시간을 절반으로 단축하다
우주 산업에서 '속도'는 곧 경쟁력입니다. 복잡한 조립 공정은 리드타임을 길게 만들고 비용을 상승시키는 주원인입니다. 2025년 9월, 최근 항공우주 거인 보잉(Boeing)은 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 3D프린팅 기술을 도입하여 위성 태양광 날개(Solar Array Wings)의 생산 시간을 획기적으로 단축하는 데 성공했습니다.
1. 부품 통합(Integration)의 마법: DfAM의 실현
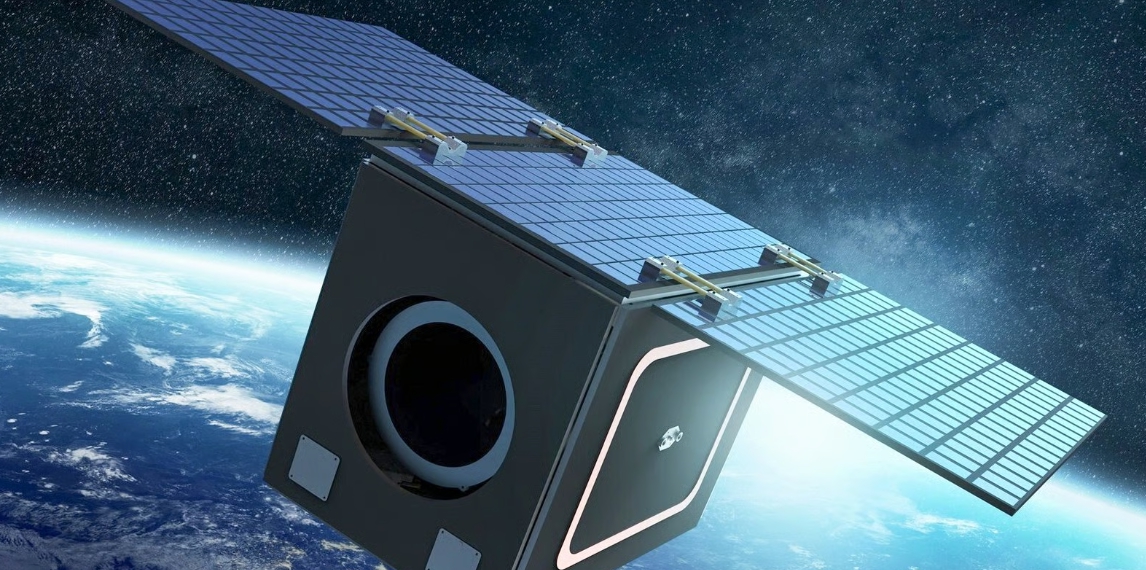

기존의 위성 제조 방식은 수많은 개별 부품을 깎고 다듬어(절삭 가공) 복잡하게 조립하는 과정을 거쳐야 했습니다. 하지만 보잉은 새로운 3D프린팅 공정을 통해 하네스 경로(Harness paths)나 부착 지점(Attachment points)과 같은 세부 기능들을 태양광 패널 기판 자체에 직접 프린팅했습니다.
이는 DfAM(적층제조특화설계)의 정수를 보여주는 사례입니다. 수십 개의 부품을 조립하는 대신, 기능이 통합된 하나의 구조물을 출력함으로써 복잡한 조립 단계를 생략하고 제조 공정을 단순화한 것입니다.
2. 납기 6개월 단축이라는 혁신
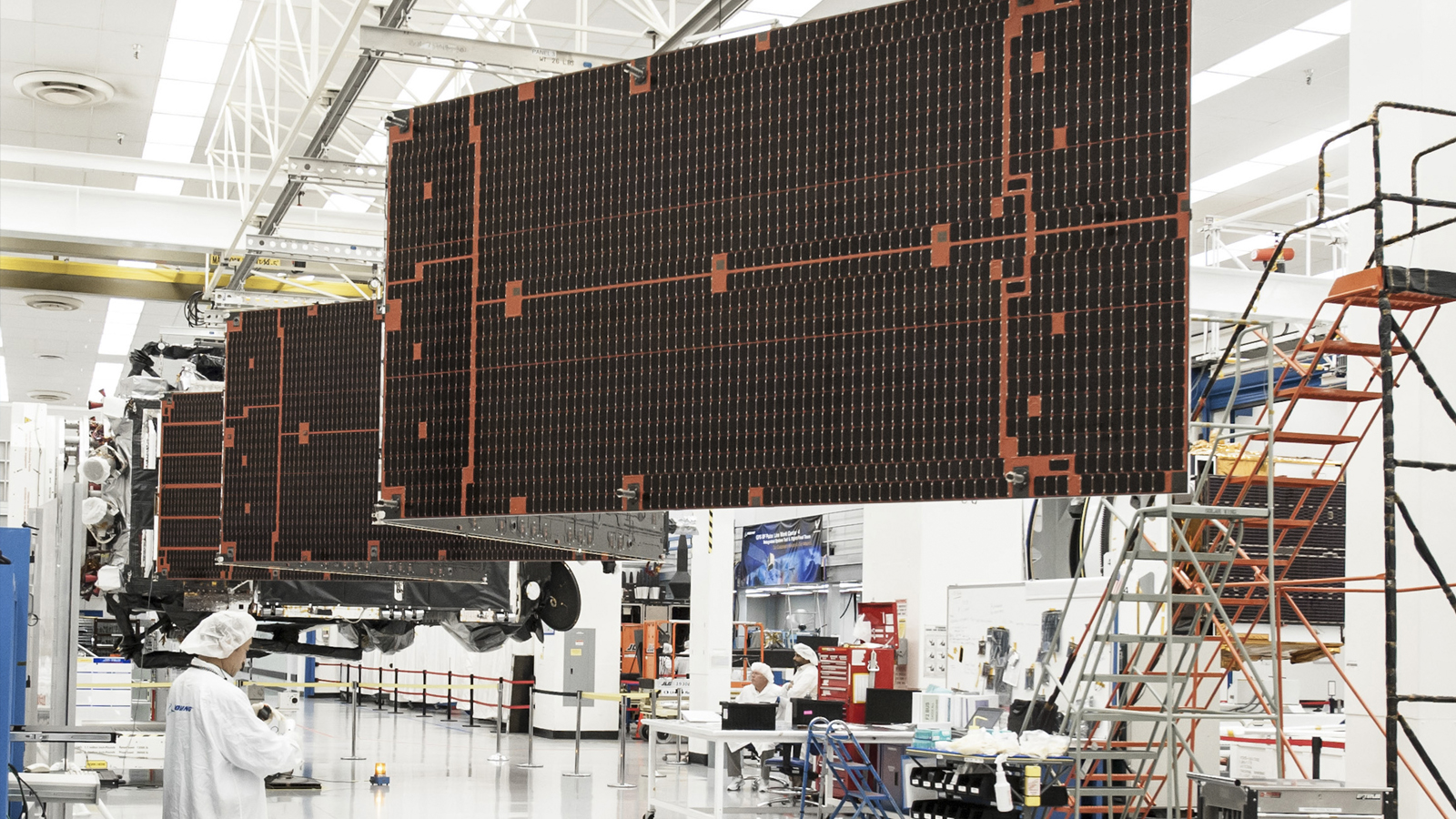
이러한 공정 혁신은 놀라운 결과로 이어졌습니다. 패널 구조와 내장 기능을 동시에 프린팅함으로써, 보잉은 전체 배송 시간을 무려 6개월이나 단축할 수 있었습니다. 보잉의 우주 임무 시스템 부사장 미셸 파커(Michelle Parker)는 "우리는 더 빠른 속도를 설정하기 위해 기업 전반에 걸쳐 효율성과 신기술을 도입했다"고 밝혔습니다. 이는 3D프린팅이 단순한 부품 제작을 넘어, 기업 전체의 R&D 및 생산 효율성을 극대화하는 핵심 전략임을 시사합니다.
NASA SpaceX-33: 우주에서의 자급자족, 그리고 초정밀의 증명
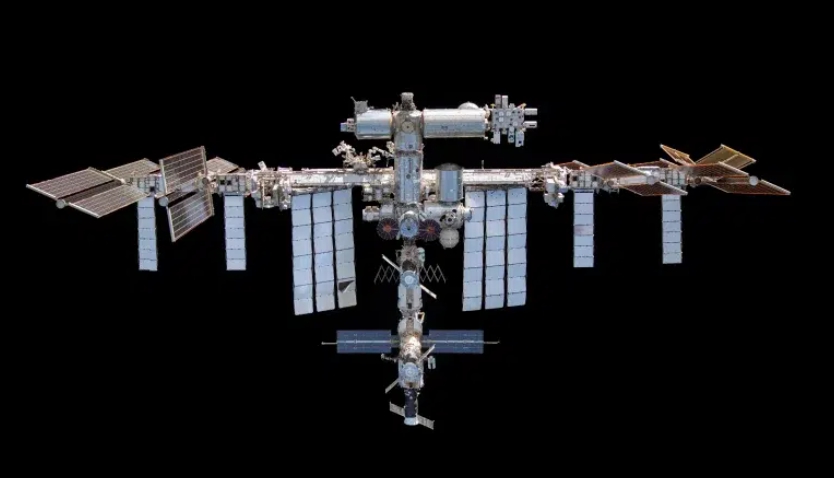

지구 밖, 국제우주정거장(ISS)에서도 3D프린팅은 핵심적인 역할을 수행하고 있습니다. 최근 NASA의 SpaceX-33 보급 임무에는 3D프린팅을 활용한 매우 흥미로운 실험들이 포함되어 있습니다.
우주라는 고립된 환경에서 필요한 부품이나 도구를 지구에서 조달받으려면 막대한 비용과 시간이 소요됩니다. NASA와 유럽우주국(ESA)은 3D프린터를 활용해 필요한 부품을 현지에서 즉시 제작하여 임무 자율성을 높이는 실험을 지속하고 있습니다. 이는 3D프린팅이 디지털 데이터만 있다면 장소에 구애받지 않고 물리적인 제품을 만들어낼 수 있는 유연한 기술임을 증명합니다.
지상에서 완성되는 우주의 꿈, 산업용 3D프린팅 제조 솔루션
누리호의 성공과 보잉, NASA의 사례에서 보듯, 우주항공 산업의 미래는 '누가 더 빠르고, 더 효율적이며, 더 복잡한 설계를 정밀하게 구현해내는가'에 달려 있습니다.

1. 복잡한 형상의 제약 없는 구현 (Design Freedom)
우주 발사체나 위성 부품은 공기 역학, 경량화, 공간 효율성을 위해 매우 복잡하고 유기적인 디자인을 필요로 합니다. 기존의 절삭 가공(CNC) 방식으로는 공구가 닿지 않는 내부 구조(Under-cut)나 복잡한 곡면을 구현하는 데 한계가 있거나 비용이 기하급수적으로 증가합니다.
2. 압도적인 리드타임 단축과 반복 검증 (Speed & Iteration)
누리호의 사례처럼 발사체 산업은 수많은 반복적인 시험과 검증(Iterative Testing)이 필수적입니다. 금형을 제작해야 한다면 설계 수정 시마다 수천만 원의 비용과 수개월의 시간이 소요됩니다.
하지만 3D프린팅은 금형 없이 디지털 설계 파일만으로 즉시 시제품을 출력할 수 있습니다. 설계 수정 후 재검증까지 걸리는 시간을 수개월에서 수일로 단축시킵니다. 이는 R&D 비용을 획기적으로 절감하고 개발 속도를 가속화하여, 빠르게 변화하는 우주 산업 트렌드에 민첩하게 대응할 수 있는 핵심 동력입니다.
3. 다품종 소량 생산에 최적화 (Low-Volume Production)
우주항공 부품은 대량 생산보다는 특수 목적에 맞는 소량 생산이 주를 이룹니다. 사천의 우주항공 기업들이 다양한 역할을 분담하여 누리호를 완성했듯, 다품종 소량 생산 시스템은 필수적입니다. 산업용 3D프린팅은 재고 부담 없이 필요한 수량만큼만 정밀하게 생산할 수 있는 주문형 생산(On-demand Manufacturing) 환경을 제공합니다. 이는 비용 효율성을 극대화하고, 급변하는 우주 산업의 수요에 유연하게 대응할 수 있게 합니다.
혁신의 여정, 글룩(GLUCK)도 함께 달리고 있습니다.
누리호의 4차 발사 성공부터 보잉과 NASA의 사례까지, 3D프린팅 기술은 하늘과 우주를 향한 인류의 도전을 현실로 만드는 핵심 동력이 되고 있습니다. 극한의 환경을 극복하고 불가능해 보이던 설계를 실현해내는 이들의 열정은 제조 산업 전반에 큰 영감을 줍니다.

글룩(GLUCK) 또한 이러한 여정에 함께하고 있습니다.
우리는 우주로 날아가는 거대한 로켓을 직접 만들지는 않지만, 지상에서 수많은 엔지니어와 디자이너들이 상상하는 혁신적인 아이디어를 가장 빠르고 정밀하게 실체화하기 위해 끊임없이 3D프린팅 R&D에 매진하고 있습니다.
우주항공 분야가 3D프린팅으로 새로운 궤도에 올랐듯, 글룩은 산업용 SLA 3D프린팅 분야에서 제조의 한계를 넓혀가고 있습니다.
대한민국 우주 산업의 눈부신 도약을 진심으로 응원하며, 글룩 또한 각자의 자리에서 세상을 바꾸는 기술 혁신을 위해 멈추지 않고 달리겠습니다.
GLUCK은 대량생산이 가능한 산업용 SLA 3D프린팅 전문 서비스 기업입니다.
작은 아이디어를 반복 가능한 생산성으로 전환해, 현실 가능한 제조 솔루션을 제공합니다.
지금 글룩에 문의해 보세요.
📩 제작 및 상담 문의: https://glucklab.com/
References
[1] Yonhap News Agency, “South Korea Advances Aerospace Capabilities with New Developments.” (online article).
Link: https://www.yna.co.kr/view/AKR20251128098300052?input=1195m
[2] Newsis, “Korean Industry Reports New Progress in Aerospace and Defense Manufacturing.” (online article).
Link: https://www.newsis.com/view/NISX20251128_0003421612
[3] VoxelMatters, “3D Printing Is at the Core of NASA’s SpaceX CRS-33 Resupply Mission.” (online article).
Link: https://www.voxelmatters.com/3d-printing-is-at-the-core-of-nasas-spacex-33-resupply-mission/
[4] All3DP, “Boeing’s 3D Printing Breakthrough Cuts Satellite Production Time in Half.” (online article).
Link: https://all3dp.com/4/boeings-3d-printing-breakthrough-cuts-satellite-production-time-in-half/
[Aerospace R&D] The Heroes of Nuri's Success, and the Manufacturing Innovation Opened by 3D Printing in the 'New Space' Era

Success of Nuri's 4th Launch: South Korea's Manufacturing Technology Soars into Space
On the early morning of the 27th, South Korea's homegrown launch vehicle 'Nuri' successfully completed its fourth flight, soaring through the night sky. This launch holds a deep meaning beyond simple success. It is the first case demonstrating the potential of 'Private-led Space Development (New Space)' in practice, with Hanwha Aerospace, a system integration company, taking charge of airframe manufacturing and participating in launch preparation and operation processes.
In particular, behind this success was the dedicated contribution of South Korea's aerospace manufacturing companies. From fuel tanks to engine support structures, and the launch vehicle's neural network of electrical connectors and insulation, this colossal challenge, possible only when tens of thousands of parts are combined without error, was achievable thanks to the world-class technology and production capabilities possessed by our manufacturing companies.
Now, the South Korean space industry is moving beyond the state-led R&D stage into a commercialization and industrialization phase led by private companies. However, this transition brings the task of 'faster, more efficient, and more precise manufacturing.' Innovation in manufacturing processes is essential to minimize launch gaps and maintain technical personnel and supply chains.
The core technology to solve these challenges and accelerate the 'New Space' era is Industrial 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing). Today, let's explore how global aerospace leaders are innovating R&D speeds using 3D printing through the latest cases of Boeing and NASA.
Boeing: Cutting Satellite Production Time in Half with 3D Printing
In the space industry, 'speed' is competitiveness. Complex assembly processes are the main cause of long lead times and rising costs. In September 2025, aerospace giant Boeing succeeded in dramatically shortening the production time of satellite Solar Array Wings by introducing 3D printing technology to solve these problems.
1. The Magic of Integration: Realization of DfAM

Traditional satellite manufacturing methods required carving and refining numerous individual parts (subtractive manufacturing) and going through complex assembly processes. However, Boeing printed detailed features such as harness paths and attachment points directly onto the solar array substrate panel through a new 3D printing process.
This is a case that shows the essence of DfAM (Design for Additive Manufacturing). Instead of assembling dozens of parts, by printing a single structure with integrated functions, the complex assembly steps were skipped and the manufacturing process was simplified.
2. Innovation of 6-Month Lead Time Reduction

This process innovation led to amazing results. By printing the panel structure and built-in functions simultaneously, Boeing was able to shorten the entire delivery time by a whopping 6 months.
Michelle Parker, Vice President of Boeing Space Mission Systems, stated, "We introduced efficiencies and new technologies across the enterprise to set a faster pace". This suggests that 3D printing is a key strategy to maximize R&D and production efficiency for the entire company, beyond simple part manufacturing.
NASA SpaceX-33: Self-Sufficiency in Space, and Proof of Ultra-Precision
Outside Earth, on the International Space Station (ISS), 3D printing is also playing a key role. Recent NASA SpaceX-33 resupply missions include very interesting experiments utilizing 3D printing.

1. Precision Manufacturing in Extreme Environments (On-demand Manufacturing)
Procuring necessary parts or tools from Earth in the isolated environment of space takes enormous cost and time. NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) are continuing experiments to increase mission autonomy by immediately manufacturing necessary parts on-site using 3D printers. This proves that 3D printing is a flexible technology that can create physical products regardless of location if digital data is available.
2. Reality from Imagination: Ultra-Precision Bio-Printing
A point to note in this mission is the 3D bio-printing experiment in a microgravity environment. Scientists are conducting ultra-precision printing experiments using living cells as raw materials to help nerve regeneration after injury or to study bone formation.
Although materials different from industrial SLA printing are used, this case shows how delicate and precise structures 3D printing technology can implement. The fact that even complex shapes like human nerve tissues or blood vessels can be realized through additive manufacturing technology is strong proof that any complex mechanical part or prototype detail required in industrial sites can be perfectly solved with industrial 3D printing.
The Dream of Space Completed on the Ground, Industrial 3D Printing Manufacturing Solution
As seen in the success of Nuri and the cases of Boeing and NASA, the future of the aerospace industry depends on 'who can implement more complex designs faster, more efficiently, and more precisely.'

1. Implementation of Complex Geometries Without Constraints (Design Freedom)
Space launch vehicles or satellite parts require very complex and organic designs for aerodynamics, lightweighting, and space efficiency. Traditional subtractive manufacturing (CNC) methods have limitations in implementing internal structures (Under-cuts) or complex curves where tools cannot reach, or costs increase exponentially.
2. Overwhelming Lead Time Reduction and Repetitive Verification (Speed & Iteration)
Like the case of Nuri, numerous repetitive tests and verifications (Iterative Testing) are essential in the launch vehicle industry. If molds have to be manufactured, costs of tens of millions of won and months of time are required for each design modification.
However, 3D printing can output prototypes immediately with only digital design files without molds. It shortens the time taken for re-verification after design modification from months to days. This drastically reduces R&D costs and accelerates development speed, becoming a key driver to respond agilely to rapidly changing space industry trends.
3. Optimization for High-Mix Low-Volume Production
Aerospace parts are mainly produced in small quantities tailored to special purposes rather than mass production. Just as aerospace companies in Sacheon shared various roles to complete Nuri, a high-mix low-volume production system is essential. Industrial 3D printing provides an On-demand Manufacturing environment that can precisely produce only the necessary quantity without inventory burden. This maximizes cost efficiency and allows for flexible responses to the rapidly changing demands of the space industry.
The Journey of Innovation, GLUCK is Running Together.

From the success of Nuri's 4th launch to the cases of Boeing and NASA, 3D printing technology is becoming a key driver making humanity's challenge towards the sky and space a reality. Their passion for overcoming extreme environments and realizing designs that seemed impossible gives great inspiration to the overall manufacturing industry.
GLUCK is also together on this journey.
We do not directly build giant rockets that fly into space, but we are constantly striving for 3D printing R&D to most quickly and precisely materialize innovative ideas imagined by numerous engineers and designers on the ground.
Just as the aerospace field has risen to a new orbit with 3D printing, GLUCK is expanding the limits of manufacturing in the industrial SLA 3D printing field. We sincerely support the dazzling leap of South Korea's space industry, and GLUCK will also run without stopping for technological innovation that changes the world in our respective places.
Contact GLUCK today.
📩 For production and consultation inquiries: https://glucklab.com/
References
[1] Yonhap News Agency, “South Korea Advances Aerospace Capabilities with New Developments.” (online article).
Link: https://www.yna.co.kr/view/AKR20251128098300052?input=1195m
[2] Newsis, “Korean Industry Reports New Progress in Aerospace and Defense Manufacturing.” (online article).
Link: https://www.newsis.com/view/NISX20251128_0003421612
[3] VoxelMatters, “3D Printing Is at the Core of NASA’s SpaceX CRS-33 Resupply Mission.” (online article).
Link: https://www.voxelmatters.com/3d-printing-is-at-the-core-of-nasas-spacex-33-resupply-mission/
[4] All3DP, “Boeing’s 3D Printing Breakthrough Cuts Satellite Production Time in Half.” (online article).
Link: https://all3dp.com/4/boeings-3d-printing-breakthrough-cuts-satellite-production-time-in-half/
#GLUCK #글룩 #3DPrinting #3D프린팅 #산업용3D프린팅 #SLA3D프린팅 #우주항공 #누리호 #누리호4차발사 #사천우주항공 #R&D #시제품제작 #보잉 #NASA #우주산업 #적층제조 #신속조형 #제조혁신 #뉴스페이스 #Industrial3DPrinting #SLA3DPrinting #Aerospace #Nuri #RnD #Prototyping #Boeing #NASA #SpaceIndustry #AdditiveManufacturing #RapidPrototyping #ManufacturingInnovation #DfAM #OnDemandManufacturing
'인사이트 (Insights)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 수면무호흡증 환자를 위한 새로운 방법, FDA가 승인한 3D프린팅 맞춤 수면 치료 기기! (1) | 2025.12.09 |
|---|---|
| 학생들의 상상이 현실이 된 순간, '2025 제2회 글룩 졸업전시 지원 프로그램' (1) | 2025.12.05 |
| 단 60일 만에 완성된 3D프린팅 슈퍼카 : 모빌리티 다이렉트 제조(Direct Manufacturing) (2) | 2025.11.25 |
| SLA 3D프린팅, 로봇 제조의 ‘맞춤형 대량생산’ 시대를 열다 (0) | 2025.11.21 |
| 애플(Apple), 3D프린팅 대량생산으로 제조 방식을 전환하다 (0) | 2025.11.19 |
